Health
Delayed cervical cancer diagnosis prompts calls for improved healthcare
Following persistent requests, Jessica underwent an MRI scan, which yielded a diagnosis indicating a need for immediate medical attention.
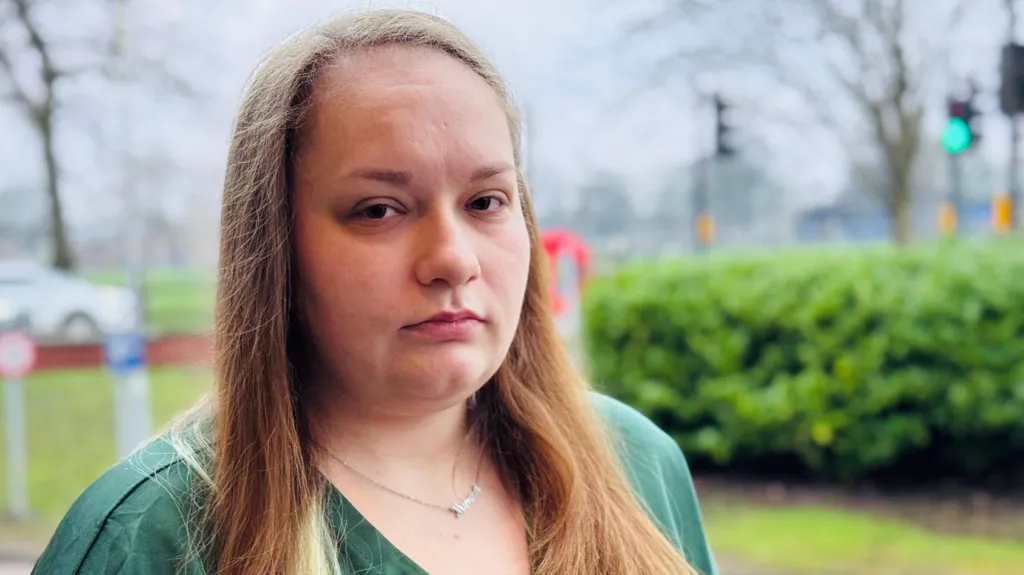
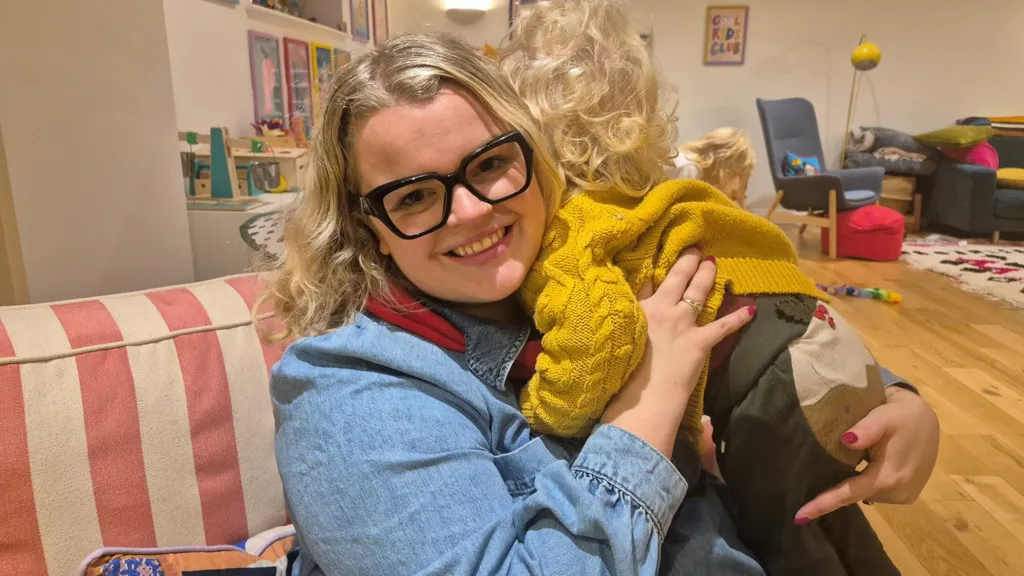
A woman who was diagnosed with cervical cancer after years of seeking medical attention has expressed her disappointment with the healthcare system, stating that she has lost trust in medical professionals.

Jessica Mason, who experienced persistent symptoms such as vaginal swelling, bleeding, and pain, claims that her concerns were initially dismissed by her GP and hospital doctors, prompting her to request a scan that ultimately revealed the presence of cancer requiring immediate treatment.
Mason, 44, believes that her persistence and emotional distress were key factors in her eventual referral for an MRI, which led to her diagnosis, saying, "I was convinced that something was wrong, and I'm grateful that I was finally taken seriously."
A recent report by the Senedd health committee has criticized the Welsh government for its handling of gynaecological cancer care, stating that women have been "let down" by the lack of action taken to address the issue.
The Welsh government has responded by stating that it is collaborating with the NHS to enhance gynaecological cancer outcomes and improve patient care.
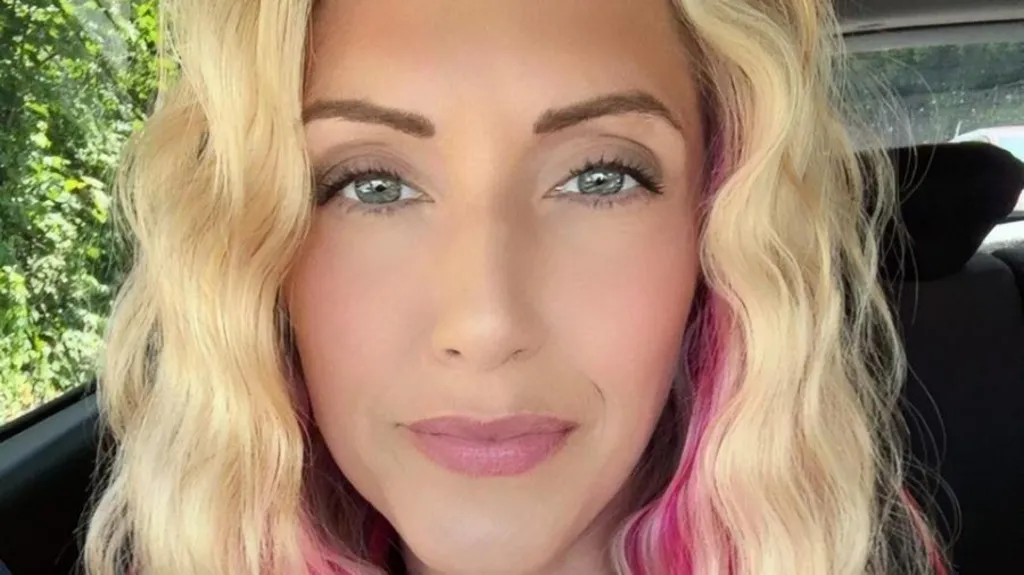
In 2019, Jessica Mason, a resident of Penarth in the Vale of Glamorgan, began experiencing severe vaginal bleeding and pain, which she brought to the attention of her healthcare providers.
Mason recalls feeling certain that something was amiss with her health, but her concerns were not initially addressed.
She underwent ultrasounds that did not detect any abnormalities, and was given various diagnoses, including a cyst, endometriosis, and prolapse, for which she was advised to perform pelvic floor exercises to alleviate her symptoms.
Mason found the experience confusing and frustrating, as she had trusted her doctors to provide an accurate diagnosis and effective treatment.
A smear test conducted six months prior to her diagnosis had also failed to detect any issues, further complicating her situation.

It was not until May 2022, when Mason visited the University Hospital of Wales in Cardiff to discuss her ultrasound results, that she became emotional and pressed her doctors to investigate her symptoms further.
At that point, her doctors offered to conduct an MRI, which Mason believes was intended to reassure her rather than address any underlying concerns.
The MRI was eventually performed, and the results were available a couple of weeks later, in June 2022.
Mason was surprised to learn that she had stage 1 B3 cervical cancer, which required immediate treatment due to the size of the tumor.
Initially, Mason had not considered the possibility of cancer, thinking that her symptoms might be caused by an infection or another less severe condition.
Her doctor informed her that the tumor was larger than 4cm (1.6in) in size, but still localized to the cervix, and that she needed to begin treatment promptly.
Mason underwent a five-week program of chemotherapy and radiotherapy starting in August 2022.
The treatment had a significant impact on her personal life, including her 13-year-old son, and forced her into early menopause, making it impossible for her to have another child.
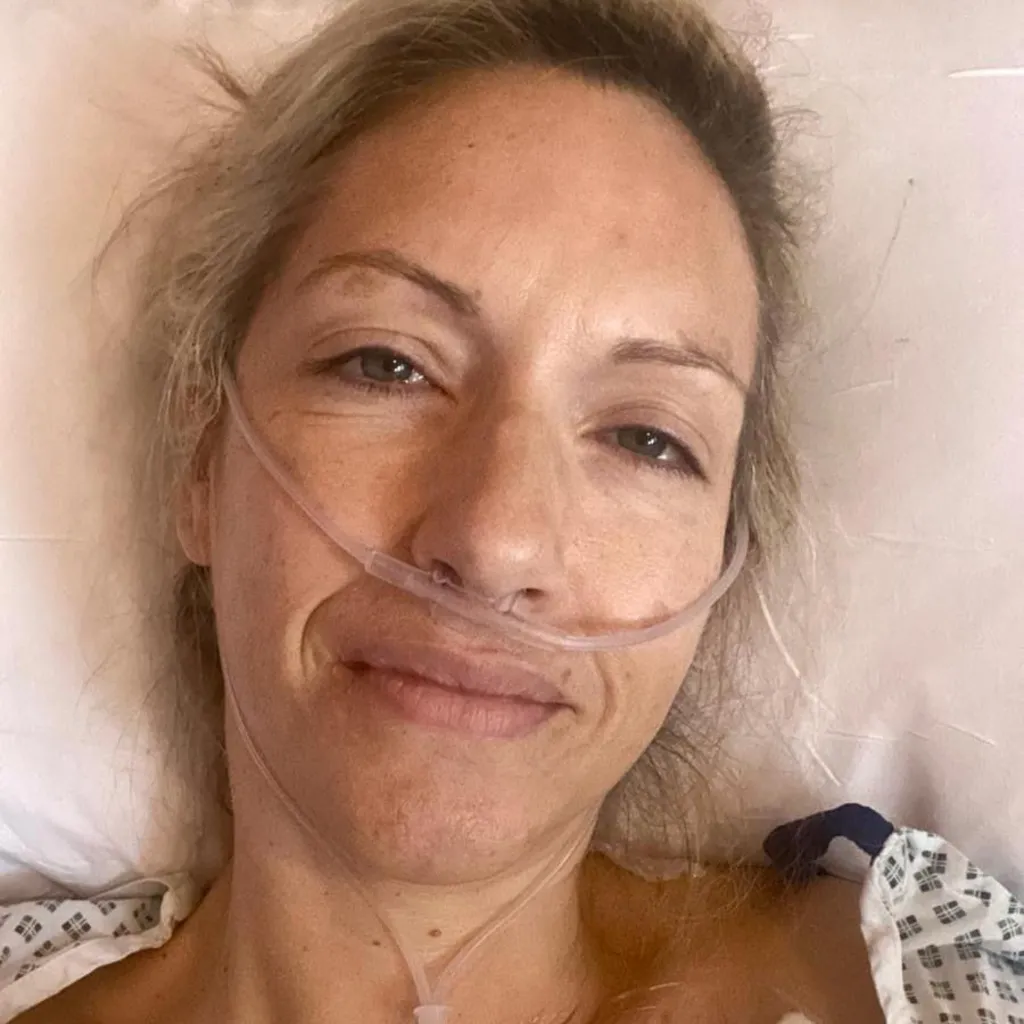
Mason found it challenging to manage her daily responsibilities, including caring for her son, due to the physical and emotional toll of her treatment.
In retrospect, Mason believes that she should have been referred for an MRI sooner, which could have potentially altered the course of her treatment.
She also pointed out that the cost of the MRI might be comparable to the expenses incurred during her prolonged period of seeking medical attention and treatment.
Unfortunately, Mason's health issues persisted, and a follow-up MRI in February 2023 revealed that the tumor was still present, necessitating a hysterectomy in July 2023.
Mason expressed her disappointment with the healthcare system, stating that she had lost faith in medical professionals due to her experiences.
She now finds herself constantly questioning the advice and treatment she receives from doctors, which has taken a toll on her mental well-being.
As a result of her health issues, Mason has had to reduce her work schedule to three days a week.
Her experience has had a profound impact on her life, affecting not only her physical health but also her relationships and overall well-being.
Mason continues to experience occasional bleeding and will require further biopsies, leaving her with a sense of uncertainty and anxiety about her future.
She is concerned that her healthcare providers might miss something critical again, which could have severe consequences for her survival.
Mason has accused the health board of delaying the release of her medical records, which she needs to consider potential legal action against them.
She believes that women's health issues are often not addressed promptly or taken seriously, with symptoms being dismissed as mere "women's problems."
A spokesperson for Cardiff and Vale University Health Board expressed regret over Mason's experience and acknowledged the challenges surrounding her cancer diagnosis.
However, due to ongoing legal proceedings, the health board declined to comment further on Mason's individual case.
A recent report by the Senedd health committee has found that women in Wales continue to face inadequate care for gynaecological cancer, despite previous recommendations to improve services.
The report highlighted the Welsh government's failure to implement key recommendations made in December 2023, including the allocation of specific funding for gynaecological cancer services and the establishment of measurable targets for improving patient outcomes.
The report noted that Wales has failed to meet waiting time targets, with only 41% of patients starting treatment within the 62-day target in October 2025.
Cancer charity Tenovus has expressed concern over the lack of progress in addressing gynaecological cancer care in Wales.
The Welsh government has stated its commitment to working with the NHS to improve access to timely diagnosis and treatment for women with gynaecological cancer.
The government acknowledged that the current performance against the 62-day target is unacceptable and must be improved.
To address these issues, the government has implemented changes to support earlier referrals and is investing in new equipment and treatments to enhance women's outcomes.
The government recognizes the need for significant improvement in the current performance and is working to address the shortcomings in gynaecological cancer care.
In Wales, a significant initiative is underway to transform the state of women's healthcare through the implementation of the Women's Health Plan.
Health
Study Explores if Brain Stimulation Can Reduce Selfish Behavior
Researchers have found a way to temporarily and marginally decrease self-centered behavior in individuals by activating two specific regions of the brain.
Researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery, finding that temporary reductions in selfish behavior can be achieved by stimulating specific areas of the brain.
A recent study conducted at the University of Zurich involved 44 participants who were tasked with dividing a sum of money between themselves and an anonymous partner, allowing scientists to observe their decision-making processes.
The experiment utilized electrical current to stimulate the frontal and parietal regions of the brain, located at the front and rear of the skull, respectively. When these areas were stimulated simultaneously, participants exhibited a greater willingness to share their funds.
According to Prof Christian Ruff, a lead author of the study, the observed effects were consistent, albeit modest in scale.
Statistical analysis revealed a notable increase in participants' willingness to allocate funds to others, indicating a shift in their behavior.
The findings not only provide insight into the neural mechanisms underlying fundamental human behavior but may also have implications for the treatment of certain brain disorders characterized by impaired social behavior.
Prof Ruff noted that some individuals struggle with profound social difficulties due to an inability to consider others' perspectives, leading to consistently selfish behavior, and suggested that this discovery could potentially be used to address such issues.
However, the effects of the brain stimulation were found to be short-lived, suggesting that repeated application may be necessary to achieve lasting changes.
Prof Ruff likened the potential effects of repeated stimulation to the benefits of regular exercise, stating that consistent application over a prolonged period could lead to significant changes in behavior, much like the physical adaptations that occur with regular gym attendance.
This latest discovery builds upon a previous study in which researchers monitored brain activity while participants engaged in a similar money-sharing game, providing a foundation for the current findings.
The earlier study identified two brain regions that appeared to be synchronized, with neural activity occurring at the same frequency, when participants made more generous decisions.
These brain areas are known to play a crucial role in decision-making and empathy, enabling individuals to distinguish between their own feelings and those of others.
When participants made selfless decisions, the regions responsible for empathy and decision-making were found to be communicating with each other.
The researchers sought to investigate whether electrical stimulation could be used to influence this communication and promote more selfless decision-making.
One participant who underwent the brain stimulation test described the experience as a gentle, soothing sensation, comparable to a warm shower or light rain on the scalp.
The participant reported making decisions while receiving the stimulation without feeling any external influence on their choices.
The discovery of a consistent neural pattern associated with selfless decision-making across multiple individuals suggests that altruism may be an innate, evolutionarily conserved trait that enables humans to care for one another.
Prof Ruff emphasized the clinical significance of this finding, highlighting the potential to modify and influence this neural mechanism.
Dr Jie Hu, a co-author of the study, noted that the research provides evidence of a causal relationship between brain activity and decision-making, demonstrating that targeted stimulation can alter an individual's sharing behavior.
By manipulating communication within a specific brain network using non-invasive stimulation, the researchers observed a shift in participants' decisions, influencing the balance between self-interest and altruism.
Addressing concerns about the potential implications of this research, Prof Ruff assured that the experiment was conducted with strict adherence to medical regulations and ethical guidelines, ensuring the well-being and informed consent of all participants.
The neuroscientist drew a distinction between the controlled, medically regulated nature of the experiment and the often-subliminal influences of social media and advertising, which can affect behavior without explicit consent.
Prof Ruff suggested that, in contrast to the experiment, the impacts of social media and advertising on brain function and behavior are often unforeseen and uncontrolled, highlighting the importance of careful consideration and regulation in such contexts.
Health
NHS Workers to Receive 3.3% Pay Increase
Labor unions have expressed displeasure, yet the government maintains that its actions showcase a dedication to its workforce.
The government has confirmed that NHS staff in England will receive a 3.3% pay increase in the upcoming financial year.

This pay award applies to approximately 1.4 million health workers, including nurses, midwives, physiotherapists, and porters, but excludes doctors, dentists, and senior management.
Although the Department of Health and Social Care initially proposed a lower figure, it has accepted the recommendation of the independent pay review body to demonstrate its commitment to NHS staff, resulting in a higher pay rise than initially suggested.
However, several health unions have expressed disappointment with the announced pay award.
Prof Nicola Ranger, general secretary of the Royal College of Nursing (RCN), noted that the 3.3% increase falls short of the current consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate of 3.4%, which measures the rise in prices over the past year.
Prof Ranger stated, "A pay award that is lower than the current inflation rate is unacceptable, and unless inflation decreases, the government will be imposing a real pay cut on NHS workers."
She criticized the government's approach, saying, "This strategy of making last-minute decisions is not an appropriate way to treat individuals who are essential to a system in crisis."
Prof Ranger indicated that she would wait to see the pay awards for the rest of the public sector and doctors before deciding on a course of action.
The RCN had previously reacted strongly to the 5.4% pay increase received by resident doctors last year, compared to the 3.6% increase received by nurses, which they described as "grotesque".
Prof Ranger emphasized, "Nursing staff will not accept being treated with disrespect, as has happened in the past when they were given lower pay awards than other groups."
Helga Pile, head of health at Unison, the largest health union, commented, "NHS staff who are already under financial pressure will be outraged by another pay award that fails to keep up with inflation."
"Once again, they are expected to deliver more while their pay effectively decreases, as it falls behind the rising cost of living," she added.
In response, the government argued that the pay award is actually above the forecasted inflation rate for the coming year, which is around 2%.
A spokesperson for the Department of Health and Social Care stated, "This government greatly values the outstanding work of NHS staff and is committed to supporting them."
The pay increase is expected to be implemented by the start of April.
However, the government did not provide a timeline for the announcement on doctors' pay, as the pay review body responsible for making recommendations on their pay has yet to submit its report to ministers.
The government is currently engaged in negotiations with the British Medical Association regarding the pay of resident doctors, previously known as junior doctors.
Members of the BMA recently voted in favor of strike action, granting them a six-month mandate for walkouts, and there have been 14 strikes so far in the ongoing dispute.
Health
NHS Waiting List Hits Three-Year Low
In England, the backlog has fallen below 7.3 million for the first time since 2023, yet worries persist regarding prolonged waiting times in accident and emergency departments.
England's hospital waiting list has reached its lowest point in almost three years, marking a significant milestone in the country's healthcare system.
As of December 2025, the number of patients awaiting treatment, including knee and hip operations, stood at 7.29 million, the lowest figure recorded since February 2023.
However, the latest monthly update from NHS England reveals that long wait times persist in Accident and Emergency departments, with a record number of patients experiencing 12-hour trolley waits.
In January 2026, over 71,500 patients spent more than 12 hours waiting for a hospital bed after being assessed by A&E staff, the highest number tracked since 2010.
This translates to nearly one in five patients admitted after visiting A&E waiting for an extended period.
According to Health Secretary Wes Streeting, while progress has been made, significant challenges still need to be addressed.
Streeting acknowledged that "there is much more to do" and emphasized the need to accelerate progress, but expressed optimism that the NHS is on the path to recovery.
Dr. Vicky Price, representing the Society for Acute Medicine, noted that hospitals are operating beyond safe capacity in terms of emergency care.
Dr. Price highlighted the vulnerability of patients who require admission, often elderly and frail individuals with complex needs, who are at greater risk of harm when care is delivered in corridors and hospitals exceed safe limits.
Duncan Burton, Chief Nursing Officer for England, commended the progress made in reducing wait times, achieved despite the challenges posed by strikes by resident doctors.
Burton attributed this progress to the hard work and dedication of NHS staff, describing it as a "triumph".
Although the waiting list decreased, performance against the 18-week target slightly declined, with 61.5% of patients waiting less than 18 weeks, compared to 61.8% in November, and still short of the 92% target set to be met by 2029.
Rory Deighton of the NHS Confederation, which represents hospitals, welcomed the progress but cautioned that it obscures significant regional variations.
A recent BBC report revealed that nearly a quarter of hospital trusts experienced worsening wait times over the past year.
Deighton emphasized that the NHS is composed of numerous separate organizations, each with unique financial and operational challenges, making it more difficult to address care backlogs in some areas.
According to Deighton, this means that tackling care backlogs will be more challenging in certain parts of the country due to these distinct regional challenges.
-

 News9 hours ago
News9 hours agoAustralian Politics Faces Questions Over Gender Equality Amid Sussan Ley’s Appointment
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoFarage Says Reform to Replace Traditional Tory Party
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoWrexham Pair Seek Win Against Former Team Ipswich
-

 News12 hours ago
News12 hours agoLiberal Party Removes Australia’s First Female Leader
-

 News10 hours ago
News10 hours agoUK Braces for Cold Snap with Snow and Ice Alerts Expected
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoHusband’s alleged £600k theft for sex and antiques blamed on drug side effects
-

 News2 days ago
News2 days agoSunbed ads spreading harmful misinformation to young people
-

 Business12 hours ago
Business12 hours agoBBC Reporter Exposed to Cyber Attack Due to Vulnerabilities in AI Coding Tool





