Health
Travelers to Cape Verde warned of stomach bug risk
Since last year, four British nationals have lost their lives due to gastrointestinal infections acquired on the archipelago.
The UK Health Security Agency (UKHSA) has issued a warning to travelers planning to visit Cape Verde, following reports of numerous British tourists falling ill with stomach bugs while in the West African archipelago.

According to the UKHSA, a total of 118 cases of shigella and 43 cases of salmonella have been identified among British travelers to Cape Verde since October 1, highlighting a significant health concern for those visiting the region.
While the majority of individuals who contract these illnesses recover within a week, a total of four British nationals have tragically died in the months following their infection, after traveling to Cape Verde for holiday.
With the February half-term break approaching, the UKHSA's warning is particularly timely, as a larger number of British travelers are expected to visit Cape Verde, a popular winter destination.
Shigella and salmonella are bacterial infections that affect the gastrointestinal system, causing symptoms such as diarrhea, fever, and stomach cramps, and can be particularly severe in certain individuals.
Although many people who contract these infections make a full recovery, certain groups, including young children, the elderly, pregnant women, and those with pre-existing medical conditions or compromised immune systems, are at a higher risk of experiencing severe symptoms and life-threatening complications.
The spread of shigella and salmonella can occur through direct contact with contaminated feces, or indirectly through the consumption of contaminated food, water, or contact with unclean surfaces.
To minimize the risk of infection, travelers to Cape Verde are advised to take precautions, including practicing good hygiene and taking steps to avoid exposure to contaminated food and water.
Dr. Gauri Godbole, deputy director for gastrointestinal infections and food safety at the UKHSA, emphasized the importance of taking simple precautions to prevent traveler's diarrhea and food poisoning, stating that such measures can significantly reduce the risk of infection.
Dr. Godbole recommended that travelers wash their hands regularly and thoroughly with soap and water or alcohol gel, particularly after using the toilet, changing diapers, and before eating or preparing food, as a key measure to prevent the spread of gastrointestinal infections.
The UKHSA has reported that the majority of shigella cases among British travelers were linked to the Santa Maria and Boa Vista areas of Cape Verde.
Santa Maria, a resort town located on Sal Island, and Boa Vista, the easternmost island in the archipelago, are popular tourist destinations, with temperatures typically reaching around 25C in February, making them attractive winter destinations.
In response to the UKHSA warning, the government of Cape Verde issued a statement indicating that, according to data collected by the country's health authorities, there is no declared outbreak of shigella in the country.
The Cape Verdean government also stated that it had not received any formal notification from the UK regarding an epidemiological outbreak originating in Cape Verde, and highlighted the country's active and coordinated health surveillance systems.
Dr. Damien Tully, an associate professor at the London School of Hygiene and Tropical Medicine, has previously noted that outbreaks of shigella are not uncommon, particularly in busy hospitality settings where large numbers of people are eating and sharing facilities.
Dr. Tully also pointed out that buffet-style catering can increase the risk of infection, as it can create an environment conducive to the spread of bacteria and viruses.
Four British nationals, including Mark Ashley, 55, from Bedfordshire, Elena Walsh, 64, from Birmingham, Karen Pooley, 64, from Gloucestershire, and a 56-year-old man from Watford, tragically died last year after contracting stomach bugs while on holiday in Cape Verde.
These four individuals are among six British tourists who have died after visiting Cape Verde since January 2023, with their families now pursuing personal injury claims against the package holiday firm Tui.
Emma Ashley, the wife of Mark Ashley, has expressed concerns about the hygiene standards at the resort where they stayed on Sal Island, highlighting the need for improved sanitation and hygiene practices.
Similarly, Sean Walsh, the son of Elena Walsh, has raised concerns about the hygiene standards at the hotel where they stayed, emphasizing the importance of ensuring that tourist facilities maintain adequate hygiene and sanitation standards.
Tui has stated that it is investigating the claims, but has declined to comment further while legal proceedings are ongoing.
Cape Verde was affected by Hurricane Erin in August, which damaged the country's water and sanitation infrastructure, and the World Health Organization has since warned of an increased risk of disease from contaminated water and carrier insects.
Health
Study Explores if Brain Stimulation Can Reduce Selfish Behavior
Researchers have found a way to temporarily and marginally decrease self-centered behavior in individuals by activating two specific regions of the brain.
Researchers have made a groundbreaking discovery, finding that temporary reductions in selfish behavior can be achieved by stimulating specific areas of the brain.
A recent study conducted at the University of Zurich involved 44 participants who were tasked with dividing a sum of money between themselves and an anonymous partner, allowing scientists to observe their decision-making processes.
The experiment utilized electrical current to stimulate the frontal and parietal regions of the brain, located at the front and rear of the skull, respectively. When these areas were stimulated simultaneously, participants exhibited a greater willingness to share their funds.
According to Prof Christian Ruff, a lead author of the study, the observed effects were consistent, albeit modest in scale.
Statistical analysis revealed a notable increase in participants' willingness to allocate funds to others, indicating a shift in their behavior.
The findings not only provide insight into the neural mechanisms underlying fundamental human behavior but may also have implications for the treatment of certain brain disorders characterized by impaired social behavior.
Prof Ruff noted that some individuals struggle with profound social difficulties due to an inability to consider others' perspectives, leading to consistently selfish behavior, and suggested that this discovery could potentially be used to address such issues.
However, the effects of the brain stimulation were found to be short-lived, suggesting that repeated application may be necessary to achieve lasting changes.
Prof Ruff likened the potential effects of repeated stimulation to the benefits of regular exercise, stating that consistent application over a prolonged period could lead to significant changes in behavior, much like the physical adaptations that occur with regular gym attendance.
This latest discovery builds upon a previous study in which researchers monitored brain activity while participants engaged in a similar money-sharing game, providing a foundation for the current findings.
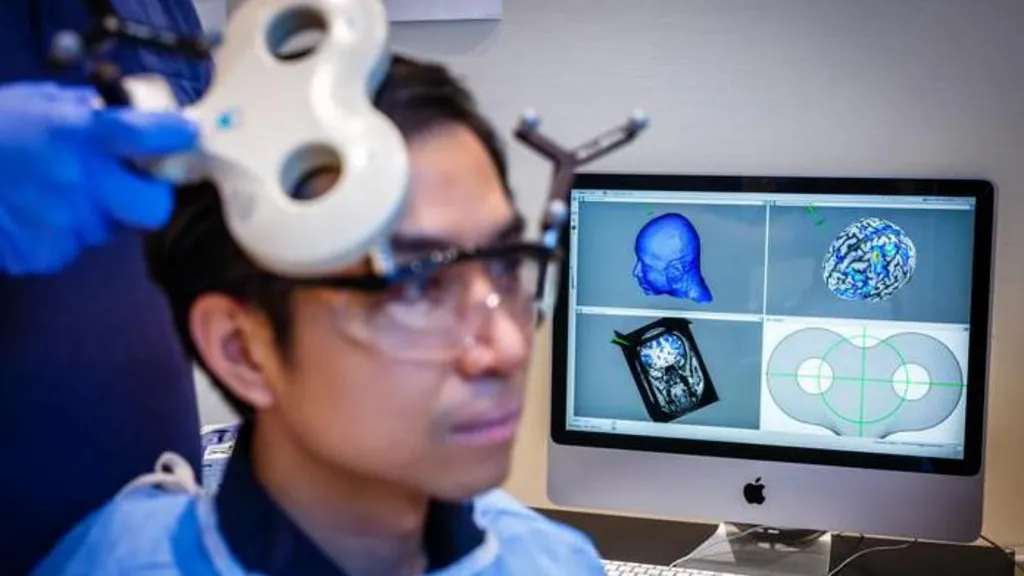
The earlier study identified two brain regions that appeared to be synchronized, with neural activity occurring at the same frequency, when participants made more generous decisions.
These brain areas are known to play a crucial role in decision-making and empathy, enabling individuals to distinguish between their own feelings and those of others.
When participants made selfless decisions, the regions responsible for empathy and decision-making were found to be communicating with each other.
The researchers sought to investigate whether electrical stimulation could be used to influence this communication and promote more selfless decision-making.
One participant who underwent the brain stimulation test described the experience as a gentle, soothing sensation, comparable to a warm shower or light rain on the scalp.
The participant reported making decisions while receiving the stimulation without feeling any external influence on their choices.
The discovery of a consistent neural pattern associated with selfless decision-making across multiple individuals suggests that altruism may be an innate, evolutionarily conserved trait that enables humans to care for one another.
Prof Ruff emphasized the clinical significance of this finding, highlighting the potential to modify and influence this neural mechanism.
Dr Jie Hu, a co-author of the study, noted that the research provides evidence of a causal relationship between brain activity and decision-making, demonstrating that targeted stimulation can alter an individual's sharing behavior.
By manipulating communication within a specific brain network using non-invasive stimulation, the researchers observed a shift in participants' decisions, influencing the balance between self-interest and altruism.
Addressing concerns about the potential implications of this research, Prof Ruff assured that the experiment was conducted with strict adherence to medical regulations and ethical guidelines, ensuring the well-being and informed consent of all participants.
The neuroscientist drew a distinction between the controlled, medically regulated nature of the experiment and the often-subliminal influences of social media and advertising, which can affect behavior without explicit consent.
Prof Ruff suggested that, in contrast to the experiment, the impacts of social media and advertising on brain function and behavior are often unforeseen and uncontrolled, highlighting the importance of careful consideration and regulation in such contexts.
Health
NHS Workers to Receive 3.3% Pay Increase
Labor unions have expressed displeasure, yet the government maintains that its actions showcase a dedication to its workforce.
The government has confirmed that NHS staff in England will receive a 3.3% pay increase in the upcoming financial year.

This pay award applies to approximately 1.4 million health workers, including nurses, midwives, physiotherapists, and porters, but excludes doctors, dentists, and senior management.
Although the Department of Health and Social Care initially proposed a lower figure, it has accepted the recommendation of the independent pay review body to demonstrate its commitment to NHS staff, resulting in a higher pay rise than initially suggested.
However, several health unions have expressed disappointment with the announced pay award.
Prof Nicola Ranger, general secretary of the Royal College of Nursing (RCN), noted that the 3.3% increase falls short of the current consumer price index (CPI) inflation rate of 3.4%, which measures the rise in prices over the past year.
Prof Ranger stated, "A pay award that is lower than the current inflation rate is unacceptable, and unless inflation decreases, the government will be imposing a real pay cut on NHS workers."
She criticized the government's approach, saying, "This strategy of making last-minute decisions is not an appropriate way to treat individuals who are essential to a system in crisis."
Prof Ranger indicated that she would wait to see the pay awards for the rest of the public sector and doctors before deciding on a course of action.
The RCN had previously reacted strongly to the 5.4% pay increase received by resident doctors last year, compared to the 3.6% increase received by nurses, which they described as "grotesque".
Prof Ranger emphasized, "Nursing staff will not accept being treated with disrespect, as has happened in the past when they were given lower pay awards than other groups."
Helga Pile, head of health at Unison, the largest health union, commented, "NHS staff who are already under financial pressure will be outraged by another pay award that fails to keep up with inflation."
"Once again, they are expected to deliver more while their pay effectively decreases, as it falls behind the rising cost of living," she added.
In response, the government argued that the pay award is actually above the forecasted inflation rate for the coming year, which is around 2%.
A spokesperson for the Department of Health and Social Care stated, "This government greatly values the outstanding work of NHS staff and is committed to supporting them."
The pay increase is expected to be implemented by the start of April.
However, the government did not provide a timeline for the announcement on doctors' pay, as the pay review body responsible for making recommendations on their pay has yet to submit its report to ministers.
The government is currently engaged in negotiations with the British Medical Association regarding the pay of resident doctors, previously known as junior doctors.
Members of the BMA recently voted in favor of strike action, granting them a six-month mandate for walkouts, and there have been 14 strikes so far in the ongoing dispute.
Health
NHS Waiting List Hits Three-Year Low
In England, the backlog has fallen below 7.3 million for the first time since 2023, yet worries persist regarding prolonged waiting times in accident and emergency departments.
England's hospital waiting list has reached its lowest point in almost three years, marking a significant milestone in the country's healthcare system.
As of December 2025, the number of patients awaiting treatment, including knee and hip operations, stood at 7.29 million, the lowest figure recorded since February 2023.
However, the latest monthly update from NHS England reveals that long wait times persist in Accident and Emergency departments, with a record number of patients experiencing 12-hour trolley waits.
In January 2026, over 71,500 patients spent more than 12 hours waiting for a hospital bed after being assessed by A&E staff, the highest number tracked since 2010.
This translates to nearly one in five patients admitted after visiting A&E waiting for an extended period.
According to Health Secretary Wes Streeting, while progress has been made, significant challenges still need to be addressed.
Streeting acknowledged that "there is much more to do" and emphasized the need to accelerate progress, but expressed optimism that the NHS is on the path to recovery.
Dr. Vicky Price, representing the Society for Acute Medicine, noted that hospitals are operating beyond safe capacity in terms of emergency care.
Dr. Price highlighted the vulnerability of patients who require admission, often elderly and frail individuals with complex needs, who are at greater risk of harm when care is delivered in corridors and hospitals exceed safe limits.
Duncan Burton, Chief Nursing Officer for England, commended the progress made in reducing wait times, achieved despite the challenges posed by strikes by resident doctors.
Burton attributed this progress to the hard work and dedication of NHS staff, describing it as a "triumph".
Although the waiting list decreased, performance against the 18-week target slightly declined, with 61.5% of patients waiting less than 18 weeks, compared to 61.8% in November, and still short of the 92% target set to be met by 2029.
Rory Deighton of the NHS Confederation, which represents hospitals, welcomed the progress but cautioned that it obscures significant regional variations.
A recent BBC report revealed that nearly a quarter of hospital trusts experienced worsening wait times over the past year.
Deighton emphasized that the NHS is composed of numerous separate organizations, each with unique financial and operational challenges, making it more difficult to address care backlogs in some areas.
According to Deighton, this means that tackling care backlogs will be more challenging in certain parts of the country due to these distinct regional challenges.
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoAustralian Politics Faces Questions Over Gender Equality Amid Sussan Ley’s Appointment
-

 News4 hours ago
News4 hours agoFarage Says Reform to Replace Traditional Tory Party
-

 News4 hours ago
News4 hours agoWrexham Pair Seek Win Against Former Team Ipswich
-

 News10 hours ago
News10 hours agoLiberal Party Removes Australia’s First Female Leader
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoUK Braces for Cold Snap with Snow and Ice Alerts Expected
-

 News4 hours ago
News4 hours agoHusband’s alleged £600k theft for sex and antiques blamed on drug side effects
-

 Business10 hours ago
Business10 hours agoBBC Reporter Exposed to Cyber Attack Due to Vulnerabilities in AI Coding Tool
-

 News7 hours ago
News7 hours agoCanadian Town Unites in Mourning After Mass Shooting Leaves Community Reeling



